More than 100,000 Google Play applications have been developed to provide minimal messaging services and promote malicious Websites as a more feature-rich non-official Telegram version.
The MobonoGram 2019 app has used the code of the legitimate Telegram Messenger and added a couple of secret scripts to support the insistence and loading of URLs received from the command server on the infected device in the application.
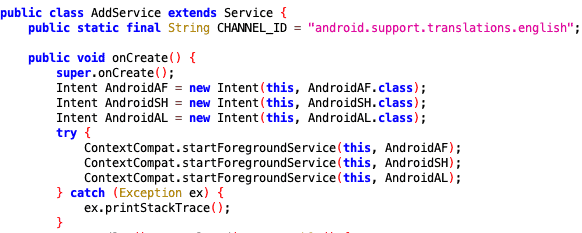
By the time the malicious app was found by security researchers, the developers–RamKal Developers–had already updated five times to the official Android store.
In the regions where the use of telegram (e.g. Russia, Iran) was prohibited and automatic starting after the booting device as well as after installing or updating an app, the users were available in English and Farsi. MobonoGram 2019 was available.
It is unclear for how long Google Play was maintained by MobonoGram 2019, but the shift to the official mobile market in Google made it possible to shift a number of installations.
The developer ensures that malicious services are in the forefront, because it has less chance of being killed by the system when low on RAM, to ensure their long-term presence in the Android system.
It was also prepared for the scenario in which the service is closed and a time counter was added for two hours and the killed service was repaid.
The malware will contact the controller to receive URLs from the infected device, a browser user agent to mask the origin and three JavaScript codes.
Regional-based sites
All user agent data received on the same server are differently according to today’s Symantec report. In addition, the URLs change based on the device’s geographical location gleaned from its IP address.
Tests have shown that when the device has a different country IP, it reacted with different types of Websites. Researchers were informed of a fake victory for a device in the US of a scam website. A Singapore gadget got a like website and other games for adults.
The researcher also made an endless observation of a loop on the same website as he asked for himself. Not only would the battery drainage be accelerated but it could also cause the device to crash.
With regard to the three JavaScript codes, Symantec analysts think the intention is to fraudulently click and increase ad revenue.
“However, the clicking events were not seen in action, even though all JavaScript codes were indeed loaded. Nonetheless, we cannot entirely dismiss the possibility of the malware being used for click fraud or some other malicious end.” – Symantec
Not only MobonoGrams 2019 is the responsibility of RamKal Developers. The same developer released another app, Whatsgram, which was the same on Google Play.
Symantec telemetric data shows 1,235 detections on their radar, deterred as Android. Fakeyouwon, relating to this malicious app; most of these have been registered in the United States, Iran, India and the United Arab States (UAE).
The malware has been found mainly in Iran, the US, the United Arab Emirates and Germany.
The malicious app is removed from Google Play but is available from Android shops of third parties. Users are advised that apps from informal markets should not be installed, as they typically rake through unwanted packages. The restriction to a trusted source of software installations can only save you a lot of trouble.











Leave a Reply