The Spelevo exploit kit has been found in a recent malicious project by safety investigators, thus infecting victims through Maze Ransomware payloads.
Maze Ransomware, a version of Chacha Ransomware, was first discovered in May by Jérôme Segura, a computer scientist who found that ransomware was distributioned with Fallout exploit kit via a fake site camouflaged as a legitimate cryptocurrency exchange app.
Segura told that attackers created a fake cryptocurrency site from Abra to buy ad network traffic that later redirected visitors to the exploit kit landing page under certain conditions. under certain conditions.
New Maze Ransomware campaign
Nao sec was the first one to notice the new Maze Ransomware project yesterday, and GrujaRS only took a closer look at the campaign one hour later.
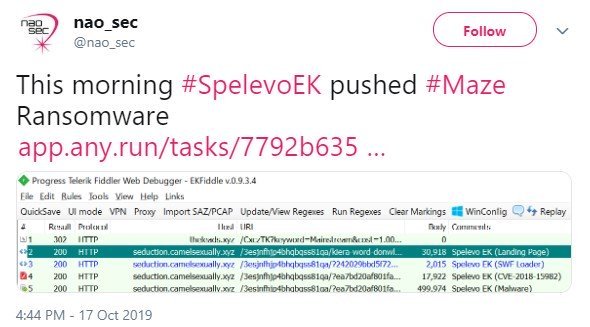
This program redirects users into the exploit kit of Spelevo, as shown in the Nao sec site requests and the screenshot below.
Once redirected to the exploit, Spelevo will try to exploit the vital use of CVE-2018-15982 in the app following free vulnerability, with users of 31.0.0.153/ 31.0.0.108 and earlier versions of flash players exposed to it.
Upon successful usage, the exploit kit downloads and installs the Maze Ransomware payload automatically via arbitrary code execution.
In the past Cisco Talos had seen Spelevo dropping the notorious IceD and Dridex bank trojans via a website that had been compromised between business and business (B2B).
 Spelevo exploit kit in action
Spelevo exploit kit in action
Maze Ransomware
If the Maze Ransomware payload is activated and executed, it will start searching for interesting files to encrypt them using RSA encryption and ChaCha20 stream cipher, e.g. documents, pictures, databases, and more, and then add several extensions as shown below.
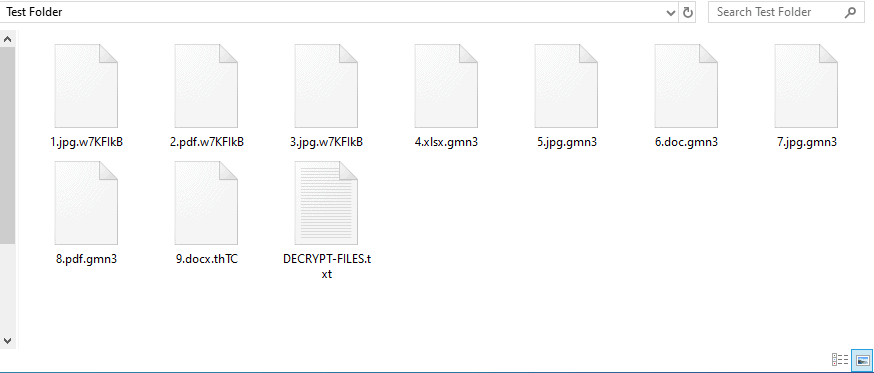
Encrypted files
The ransomware will also generate the DECRYPT-FILES.txt ransom note in each of the scanned directories, which will warn victims to open a website hosted in the TOR network, for payment instructions, to buy a private key for decrypting the data.
Victims also have an online decryption tool that helps them to decrypt three of their now locked files as confirmation that decryption is indeed possible.
According to the support site of Ransomware, the restitution cost is multiplied automatically if the victim does not pay within around a week of the restitution notice being published.
There is also a second page accessible via the clear net, claiming that it might be blocked in certain countries and therefore leaving the TOR site as the only alternative.
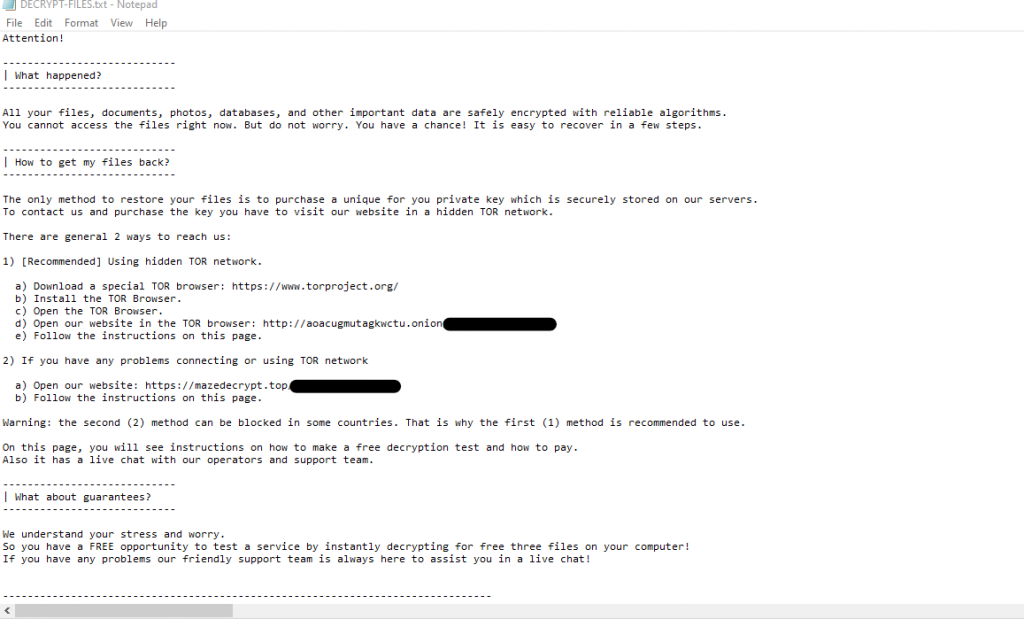 Ransom note
Ransom note
The victims will be required to post their ransom note on this support website to receive further information on how to get their data back.
The parsers can guide them to a site where they can check the decryption method for the intruder (only supporting BMP, JPG, GIF, and PNG image files) and get the details on how to buy the ransom from Bitcoins.
The website of Maze Ransomware is also supported by a live support chat that is outlined in the ransom note and found by GrujaRS.
He created a video to demonstrate how Maze Ransomware encrypts the files of his victims, how the live chat operates and how Maze Ransomware’s test decoding method can be displayed.
There is no way to openly decrypt the files that Maze Ransomware encrypts at this point. We will publish a new report with additional results if anything changes.
How to guard against Maze Ransomware
It is critical that good computer habits and security software are used in order to protect yourself from Maze Ransomware and any other ransomware families. The most important thing is that you always have a secure and checked data backup that you can recover easily, such as a ransomware attack, in case of an emergency.
Because Maze is dropped using Exploit kits, you need the most recent security patches from Windows installed and up-to-date code. It prevents you from leveraging previously patched vulnerabilities to hack your computer.
Because ransomware is also known to be distributed by compromised services from the Remote Desktop, ensure that remote computers in your network are not directly linked to the Internet by putting them behind VPNs so that only trustworthy users have access.
Running a security software with an integrated behavior detection engine such as Emsisoft Anti-Malware and Malwarebytes Anti-Malware is also important to prevent ransomware infections.
Last but not least, good online security practices must also be followed, since the most important measures are in many cases:
- Backup, Backup, Backup!
- Do not open attachments if you do not know who sent them.
- Do not open attachments until you confirm that the person actually sent you them,
- Scan attachments with tools like VirusTotal.
- Make sure all Windows updates are installed as soon as they come out! Also make sure you update all programs, especially Java, Flash, and Adobe Reader. Older programs contain security vulnerabilities that are commonly exploited by malware distributors. Therefore it is important to keep them updated.
- Make sure you use have some sort of security software installed.
- Use hard passwords and never reuse the same password at multiple sites.
- If you are using Remote Desktop Services, do not connect it directly to the Internet. Instead make it accessibly only via a VPN.











Leave a Reply