Hackers violate MSPs using the SecureAnywhere webroot console for Sodinokibi Ransomware to infect client PCs.
A Ransomware gang broke at least three managed service suppliers’ (MSPs) infrastructure and used their remote management instruments, namely the SecureAnywhere Webroot console, to implement ransomware in MSPs ‘ customers ‘ applications.
The ranching infections were first recorded today in a Reddit chapter for MSPs–businesses that provide remote IT facilities and worldwide help to businesses.
Kyle Hanslovan, Co-Founder and CEO, was online and was helpful in investigating the occurrences for some of the affected MSPs.
HACKERS GOT IN VIA RDP
Hanslovan said that hackers violated MSPs via exposed RDPs (Remote Desktop Endpoints) as well as higher privileges within compromised systems.
The hackers searched Webroot SecureAny place accounts, remote administration (consol) software used by MSPs to handle remotely located workstations (in their customers ‘ networks) in the next step of the assault.
Hanslovan says that hackers used a Powershell script on remote workstations on the console, which was used to download Sodinokibi ransomware and install it.
At least three MSPs have been hacked like this, according to the CEO of Huntress Lab. In some instances, hackers may have used a remote management console of Kaseya VSA, but this has never been officially verified.
“Only the hosts operating Webroot have been infected by two firms,” Hanslovan said.
WEBROOT DEPLOYS 2FA FOR SECUREANYWHERE ACCOUNTS
Later in the day webroot started to forcibly enable twofactor Authentication (2FA) for SecureAnywhere accounts, in accordance with the email obtained in Hanslovan, in order to avoid hacking hackers from useing the Webroot management console, which is a possible attack vector.
2FA is supported by SecureAnywhere but the function is not activated.
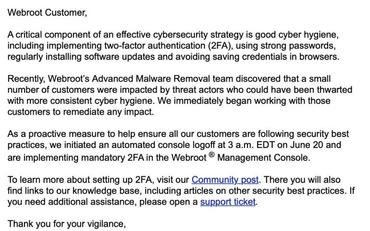
Image: Kyle Hanslovan
“Webroot’s Advanced Malware Removal team recently found that a number of clients have been affected by a threatening actor exploiting the mixture of authentication and RDP’s weak cyber hygiene procedures,” said Chad Bacher, Products SVP of WEBROOT, Carbonite corporation.
“It was time to impose two-factor authentication mandatory to ensure that the entire Webroot customer community had the best possible protection. We did so by conducting a console logo on the morning of June 20 and updating software,” he added.
“The two-factor authentication (2FA) is a good practice for cyber hygiene and we encouraged customers for a while to use the integrated 2FA Webroot Management Console. We always follow the threat environment closely and take action such as this to ensure the maximum possible protection of customers.” At that moment, a threat actor used the zero-day Oracle WebLogic to enter business networks and use the ransomware.
The event today is also the second significant wave of assaults where hackers have misused MSPs and their remote management instruments to deploy rankings on networks of their clients.
The first event took place in mid-February, when a hacker group deployed the GandCrab ransomware on its customer workstations using vulnerabilities in common MSP instruments.
Coincidentally, when this occurrence was detailed on Reddit, local Romanian media reported that in the capital of the country, five hospitals were infected with ransomware. However, outside the infection time frame, there is no proof that two occurrences are connected.
Webroot declaration updated article.











Leave a Reply